Quick Sort
快速排序是C.R.A.Hoare于1962年提出的一种划分交换排序。它采用了一种分治的策略,通常称其为分治法(Divide-and-ConquerMethod)。
https://www.zybuluo.com/Zh1Cheung/note/1076005
核心思想就是,找到pivot 然后用这个pivot作为base , 通过双指针的方法,左右移动到pivot,确保,左边的数值全部小于pivot ,右面的数值全部大于pivot,然后再通过divide conquer 进行左右两部分的后续操作,直到不能拆分pivot为止。
代码小技巧:左指针移动比较完成后,一定要落回P点,如果数据都是小于p的。所以合理处理 =
难点: 你的第一次while循环之后,并不能保证此时所有小于分割处的数字在它的左边,大于的在它数在它的右边。
如果只有两个数值的时候,就回出现,left = p 在同一点。
while (left <= right && A[left] < pivot) 循环滑动技巧
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/34479151时间复杂度:
在最优情况下,Partition每次都划分得很均匀,如果排序n个关键字,其递归树的深度就为.log2n.+1(.x.表示不大于x的最大整数),即仅需递归log2n次,需要时间为T(n)的话,第一次Partiation应该是需要对整个数组扫描一遍,做n次比较。然后,获得的枢轴将数组一分为二,那么各自还需要T(n/2)的时间(注意是最好情况,所以平分两半)。于是不断地划分下去,我们就有了下面的不等式推断。
T(n)≤2T(n/2) +n,T(1)=0
T(n)≤2(2T(n/4)+n/2) +
n
=
4T
(n/4)+2n
T(n)≤4(2T(n/8)+n/4) +
2n
=
8T
(n/8)+3n
……
T(n)≤nT(1)+(log2n)×
n
=
O
(nlogn)
也就是说,在最优的情况下,快速排序算法的时间复杂度为O(nlogn)。
在最坏的情况下,待排序的序列为正序或者逆序,每次划分只得到一个比上一次划分少一个记录的子序列,注意另一个为空。如果递归树画出来,它就是一棵斜树。此时需要执行n‐1次递归调用,且第i次划分需要经过n‐i次关键字的比较才能找到第i个记录,也就是枢轴的位置,因此比较次数为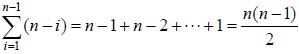 ,最终其时间复杂度为O(n2)。
,最终其时间复杂度为O(n2)。
平均的情况,设枢轴的关键字应该在第k的位置(1≤k≤n),那么:
Last updated
Was this helpful?